The importance of maintaining adequate levels of vitamin B6 for optimal brain performance cannot be overstated. Research conducted by a team from Würzburg University Medicine has shed light on the negative effects of low vitamin B6 levels on the brain. Various mental illnesses have been linked to a deficiency in vitamin B6, including impaired memory and learning abilities, depressive mood, and even genuine depression. Additionally, in older individuals, insufficient levels of vitamin B6 have been associated with memory loss and dementia.
While increasing the intake of vitamin B6 through supplements may seem like a simple solution, it is not enough to prevent or treat brain function disorders. The exact role of vitamin B6 in mental illness remains largely unclear, highlighting the complexity of brain metabolism and the need for innovative approaches to addressing these issues. Recognizing the limitations of traditional methods, researchers have explored alternative ways to enhance the availability of vitamin B6 in cells.
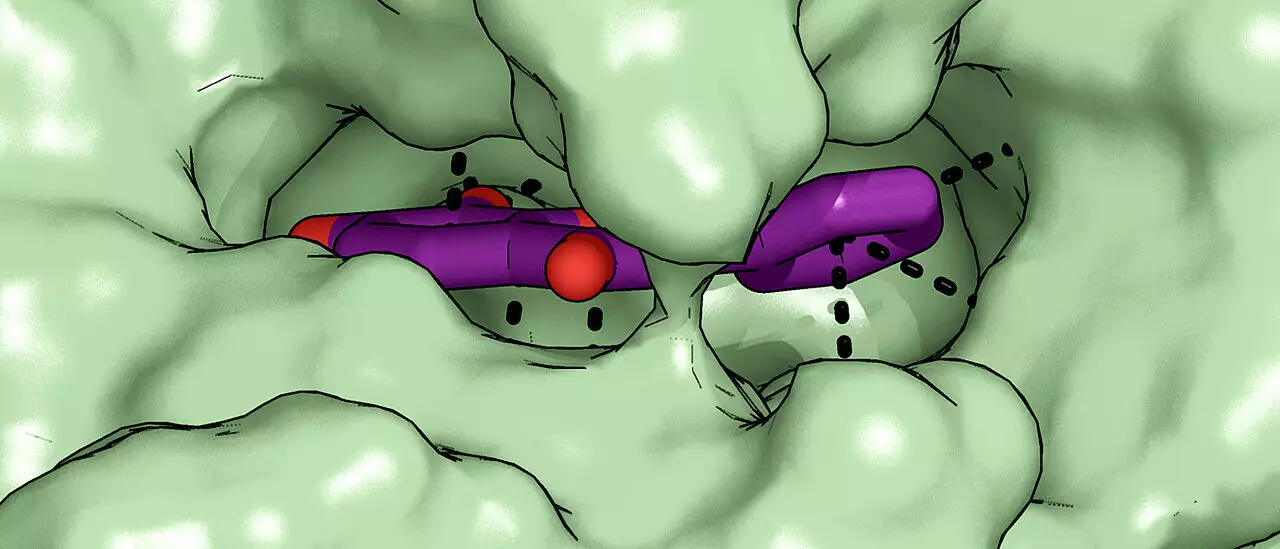
A breakthrough discovery by the research team at Würzburg University Medicine involves inhibiting the intracellular degradation of vitamin B6 to increase its levels more effectively. By specifically targeting the enzyme pyridoxal phosphatase responsible for breaking down vitamin B6, researchers have identified a natural substance called 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone that can inhibit the enzyme and slow down the degradation process.
The findings of this study have far-reaching implications for the treatment of mental disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone, known for its ability to improve learning and memory processes in disease models, has now been revealed as an inhibitor of pyridoxal phosphatase. This new understanding opens up possibilities for developing targeted drug therapies that could increase cellular vitamin B6 levels and potentially address brain disorders more effectively.
Although it is still early to determine the exact timeline for implementing these findings in clinical practice, there is growing optimism about the potential benefits of combining vitamin B6 with inhibitors of pyridoxal phosphatase. The research team is now focused on refining the development of enhanced inhibitors to precisely target the enzyme and maximize their effectiveness in increasing vitamin B6 levels in nerve cells.
The discovery of novel ways to boost vitamin B6 levels and improve brain function represents a significant advancement in the field of mental health research. By addressing the underlying mechanisms that contribute to brain disorders, such as the degradation of vitamin B6, researchers are paving the way for new treatment approaches that could benefit individuals affected by these conditions. The ongoing efforts to develop more targeted therapies hold promise for a future where mental disorders and neurodegenerative diseases are better understood and effectively managed.

Leave a Reply