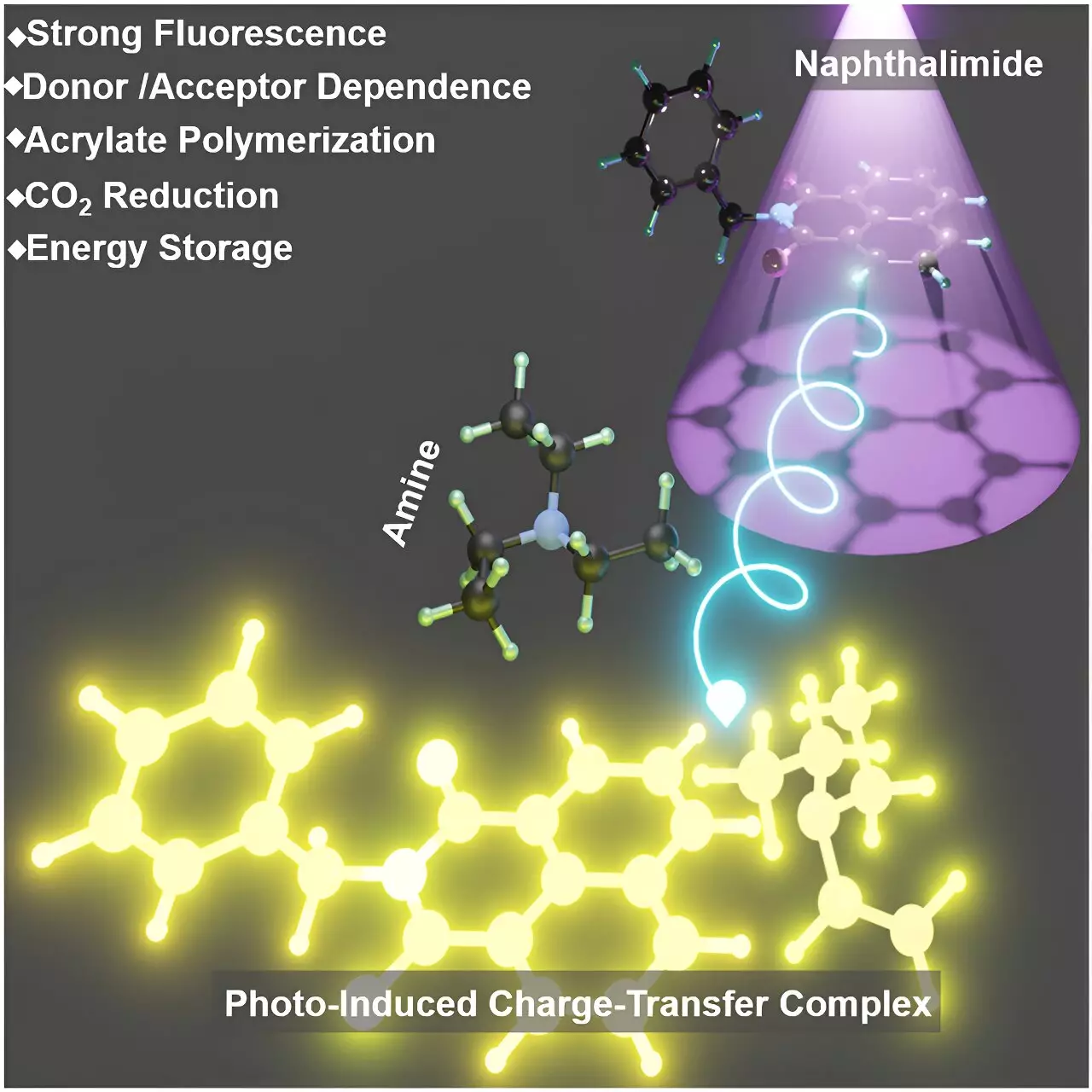
A recent study conducted by a research team led by Prof. Zhang Guoqing at the University of Science and Technology of China has shed light on the discovery of highly reactive photo-induced charge-transfer complexes (PCTCs) between amines and imides. These complexes, formed when aromatic imides and alkyl amines are exposed to UV light, have opened up new possibilities in the field of photochemical processes.
The researchers utilized various spectroscopic techniques to confirm the formation and stability of these PCTCs. Through high-resolution mass spectrometry and time-resolved spectroscopy, it was revealed that the interaction between naphthalimide and triethylamine resulted in the formation of a stable complex with distinct absorption bands and enhanced fluorescence characteristics.
Practical Applications
One of the most intriguing applications of PCTCs is their ability to initiate the polymerization of acrylic esters under UV light. This highlights the potential of these complexes in creating new polymeric materials with unique properties. Moreover, PCTCs have shown efficacy in reducing carbon dioxide, addressing crucial environmental challenges and contributing to the development of sustainable energy sources.
Another significant finding is the capability of PCTCs to store UV energy and release it in the absence of light. This feature enables processes that were traditionally dependent on continuous light exposure to proceed even in the dark. This opens up new avenues for practical applications in polymer science, environmental technology, and energy storage.
The discovery of highly reactive photo-induced charge-transfer complexes between amines and imides under UV light has not only enhanced our understanding of photo-induced charge-transfer processes but has also paved the way for practical applications in various fields. The potential of PCTCs in creating new materials, reducing carbon dioxide, and storing energy opens up exciting possibilities for innovation and sustainability. This research represents a significant advancement in the field of photochemistry, with implications for a wide range of applications in the future.

Leave a Reply