The effects of climate change go beyond just warming temperatures and rising sea levels. Recent research conducted by scientists at ETH Zurich has shed new light on how climate change is impacting the Earth’s rotation. Using advanced AI methods, researchers have been able to provide a comprehensive explanation for the long-term polar motion caused by climate change and global warming.
Climate change is leading to the melting of ice masses in Greenland and Antarctica, causing water to flow into the oceans and redistribute mass across the planet. This shift in mass is affecting the Earth’s rotation, similar to a figure skater extending their arms during a pirouette. The law of conservation of angular momentum governs the Earth’s rotation, resulting in slower rotation and longer days. The increase in the length of the day is minimal but significant.
While tidal friction caused by the moon has historically influenced the Earth’s rotational speed, the new research indicates that the impact of climate change may surpass that of the moon. If greenhouse gas emissions continue at current rates, the Earth’s rotational speed could be significantly altered. This highlights the significant impact that human activities have on the planet’s natural processes.
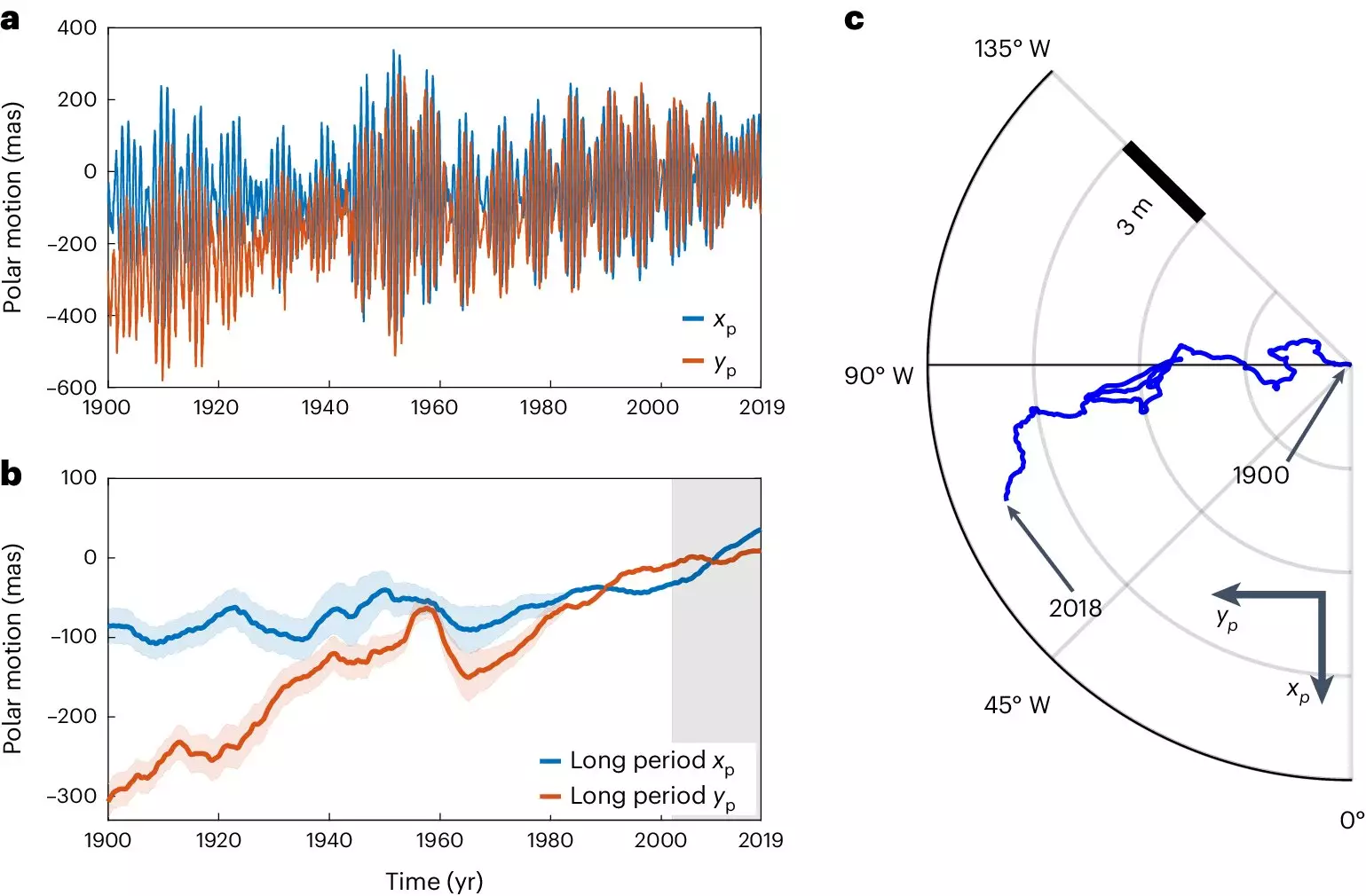
In addition to affecting the Earth’s rotational speed, climate change is also altering the axis of rotation. The melting ice sheets and movements in the Earth’s interior are causing shifts in mass that result in changes to the axis of rotation. Over time, polar motion can be observed, with points on the Earth’s surface shifting several meters every hundred years. The interconnected processes on and within the Earth play a crucial role in determining polar motion.
The research conducted by ETH Zurich scientists reveals that the Earth’s systems are intricately connected, with climate change influencing processes deep within the Earth’s core. The feedback mechanisms between climate change and the conservation of angular momentum can lead to changes in the dynamics of the Earth’s core. These findings suggest that ongoing climate change may have a broader impact than previously thought, reaching deep into the Earth’s interior.
While the effects of climate change on the Earth’s rotation are relatively subtle, they have practical implications for activities such as space exploration. Even minor changes in the Earth’s rotation can have significant consequences when navigating in space, such as sending space probes to other planets. Understanding and accounting for these effects are crucial for ensuring the success of space missions and accurate navigation.
The research conducted by ETH Zurich scientists highlights the complex interactions between climate change and the Earth’s rotation. The study provides valuable insights into how human activities are altering fundamental processes on our planet and emphasizes the need for sustainable practices to mitigate these impacts. By understanding the relationship between climate change and Earth’s rotation, we can work towards a more sustainable future for our planet and all its inhabitants.

Leave a Reply