For the past 23 years, the International Space Station (ISS) has served as a vital research center and home for astronauts from around the world. However, its days are now numbered, with NASA recently announcing a plan to pay SpaceX up to $843 million to help decommission the ISS. This move marks a significant shift in the space exploration landscape and raises questions about the future of human spaceflight.
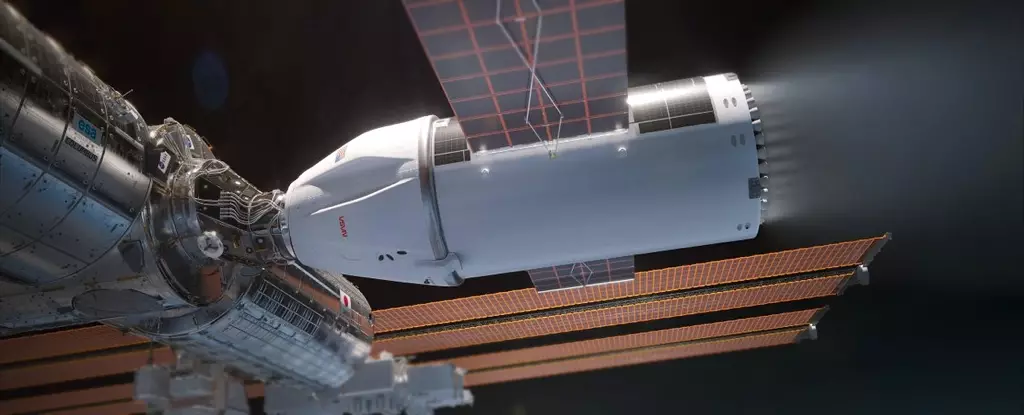
SpaceX’s involvement in decommissioning the ISS centers around the development of a superpowered, extra-large Dragon spaceship. This new vehicle is designed to push the ISS out of orbit and into a controlled descent to a remote ocean location, likely in 2031. The upgraded Dragon will feature 46 Draco engines – 30 more than a regular Dragon – and will carry six times as much propellant as a standard Dragon ship. This increased power is necessary to safely navigate the ISS through its final burn and descent.
Sarah Walker, SpaceX’s director of Dragon mission management, highlighted the complexity of the final burn required to push the ISS on the correct trajectory for its descent. This maneuver must overcome torques and forces caused by atmospheric drag on the space station to ensure a precise landing in the remote ocean. The goal is to avoid any risk of the ISS crashing in populated areas, emphasizing the need for meticulous planning and execution.
While NASA has not specified the exact location of the ISS’s final descent, it is expected to be in a remote part of the ocean, such as the South Pacific. This decision reflects the need to minimize potential hazards and ensure a controlled end to the ISS’s operational life. The choice of location is crucial in guaranteeing the safety of the deorbit process and mitigating any environmental impact.
The decommissioning of the ISS marks a significant milestone in the history of human spaceflight. It signifies the end of an era for the iconic space station and paves the way for future missions and collaborations in low Earth orbit. SpaceX’s role in this process underscores the company’s expanding presence in the space industry and its commitment to innovation and technological advancement.
Looking ahead, NASA and its international partners plan to transition towards new space stations and platforms for continued research and exploration. Private companies like SpaceX are expected to play a key role in this evolution, with NASA aiming to become one of many customers on commercial space stations in the coming years. This shift represents a new era in space exploration, characterized by collaboration, innovation, and diverse opportunities for scientific discovery.
The decommissioning of the ISS and SpaceX’s involvement in this process herald a new chapter in human spaceflight. As we bid farewell to the iconic space station, we look towards a future filled with exciting possibilities and groundbreaking discoveries in space exploration.

Leave a Reply