The Southern Ocean surrounding Antarctica is a critical region for conserving biodiversity. A team of scientists led by the University of Colorado Boulder has identified 30 new areas that are essential for protecting native wildlife in this remote and harsh environment. Without greater protection to limit human activities in these areas, the researchers warn that the region could face significant population declines.
Climate change is already impacting the Southern Ocean as warming temperatures lead to the melting of sea ice. This, in turn, has increased fishing and tourism activities in the area. These human activities not only compete with wildlife for resources but also introduce invasive species and diseases that the native wildlife is ill-equipped to handle. The delicate balance of the ecosystem is at risk as these factors threaten the survival of many species in the region.
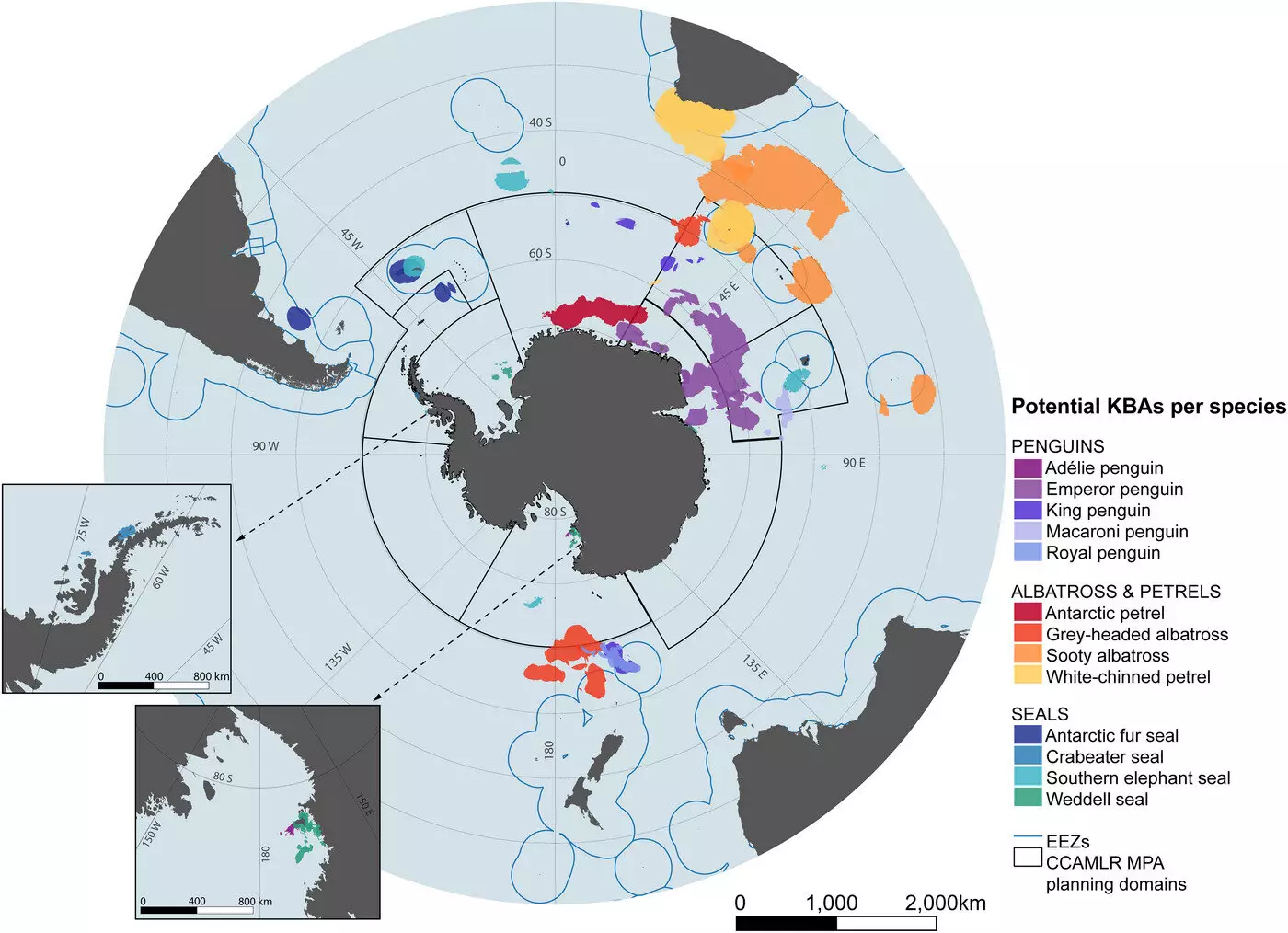
In an effort to address these challenges, the researchers set out to identify Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) in the Southern Ocean that are crucial for the survival of various species. By using existing tracking data for 13 Antarctic and sub-Antarctic seabirds and seals, they pinpointed 30 KBAs that represent vital marine habitats for foraging, breeding, and migration. This approach provided a more detailed and tailored understanding of the specific needs of individual populations, which previous conservation efforts at a large scale had overlooked.
The researchers hope that their findings will inform international bodies and governments when developing conservation strategies and determining areas where fishing should be restricted. By reducing fishing and tourism interactions in these key biodiversity areas, there is a potential opportunity to help these animals adapt and become more resilient to the impacts of climate change. It is critical for countries and organizations to work together to protect these vulnerable ecosystems and ensure the long-term survival of the species that call the Southern Ocean their home.
The Southern Ocean plays a pivotal role in mitigating the effects of climate change. It absorbs a significant amount of human-generated carbon dioxide emissions and excess heat from global warming. Protecting the biodiversity in this region is not only essential for preserving wildlife but also for maintaining the overall health of the planet. The interconnectedness of ecosystems across the globe underscores the importance of conservation efforts in even the most remote and seemingly isolated areas like the Southern Ocean.
The conservation of biodiversity in the Southern Ocean is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention and action. By identifying and protecting key areas that are critical for species survival, we can help safeguard the delicate balance of this unique ecosystem. International cooperation and strategic conservation efforts are essential in ensuring the long-term viability of the Southern Ocean and its inhabitants. It is up to us to act now to preserve the biodiversity of this vital region for future generations to enjoy.

Leave a Reply