Climate change continues to be one of the most pressing challenges of our time, influencing weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems around the globe. A recent study leveraging a unique 627-year coral record from Fiji offers unprecedented insights into ocean temperatures and climate variability across the Pacific Ocean. This groundbreaking research, published in the journal *Science Advances*, highlights how anthropogenic climate change interacts with long-established climatic trends and variability, reshaping our understanding of past and present climate dynamics.
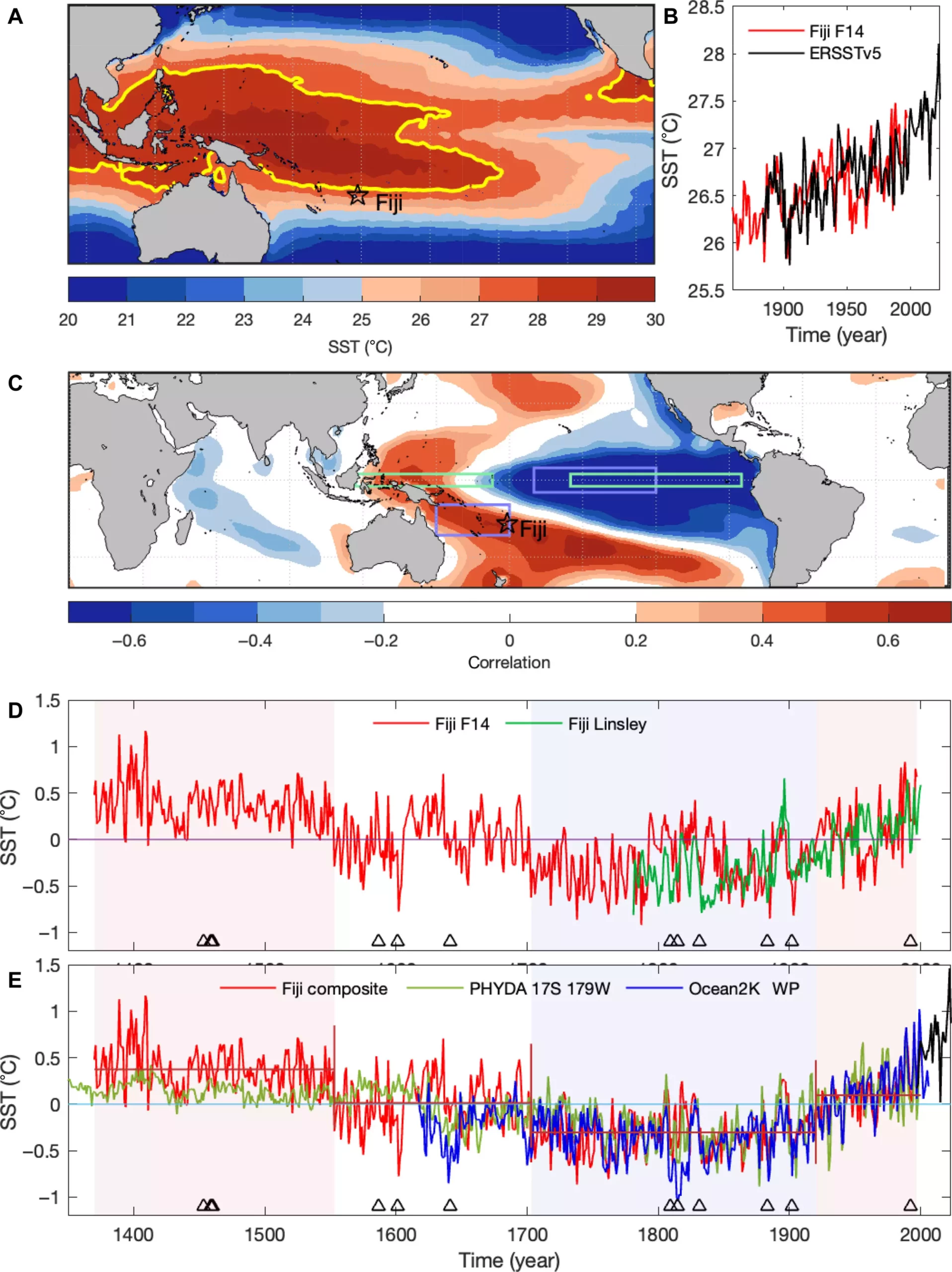
Corals, as living organisms, are exceptional at preserving environmental conditions over extended periods. Researchers were able to reconstruct a continuous sea surface temperature record from coral samples taken from a giant boulder coral species, *Diploastrea heliopora*, found in the Fijian Archipelago. The technique involves geochemical analysis of the strontium-to-calcium (Sr/Ca) ratio in the coral, which serves as a reliable proxy for past ocean temperatures. This method has yielded what is reportedly the longest continuous record of sea surface temperatures to date, allowing for a nuanced examination of climatic changes over nearly seven centuries.
The research indicates fluctuating ocean temperatures, with a notable warm period occurring between 1380 and 1553. This time frame exhibited temperatures comparable to those recorded during the late 20th century. However, the most striking finding is that the ocean temperatures documented since 1920 mark a significant departure from the natural variability observed in earlier centuries. Presently, ocean temperatures in the Pacific have reached levels not seen in over 650 years, underscoring a worrying trend linked to human activities, particularly greenhouse gas emissions attributed to industrialization and deforestation.
The study, led by an international team including experts from Monash University and the National Autonomous University of Mexico, uncovers critical connections between long-term climatic variability and modern climate change. By reconstructing patterns of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation, the researchers were able to reveal the interplay between natural fluctuations and anthropogenic warming that has occurred over the past century. This comprehensive analysis lays the groundwork for understanding how ongoing changes in the climate system are likely to affect weather patterns and lead to more extreme weather events.
Dr. Ariaan Purich emphasized the importance of understanding long-term climate variability for predicting future changes in climate. As temperature variations across the Pacific influence the broader global climate system, the implications for local communities, especially those in vulnerable Pacific Island nations, cannot be overstated. The anticipated shifts toward a drier climate in the Coral Sea region have significant ramifications for agricultural practices, freshwater availability, and the overall resilience of these communities.
The findings from this comprehensive coral study serve as a clarion call for concerted action to mitigate climate change. The research not only provides critical insights into the historical context of ocean temperatures but also strengthens the case for limiting global warming to 1.5°C. Strategies to achieve this include the global transition to renewable energy sources, electrification of economies, and urgent reductions in reliance on coal and gas. The local effects observed in the Pacific Islands could foreshadow challenges faced by broader global ecosystems and populations unless decisive action is taken.
This study reveals the complexities of climate change as it intertwines historical climatic patterns with modern challenges. By understanding how past ocean conditions and climate variability have shaped the current environment, we can work towards better predictive models and develop strategies to combat adverse climate impacts. The results not only enrich our knowledge of past climate behavior but also pave the way for future research dedicated to solving one of humanity’s greatest challenges—navigating the uncertain waters of climate change.

Leave a Reply