Optical spectrometers have long been essential instruments in various fields, from medical diagnosis to material characterization. However, traditional spectrometer designs have been limited by their bulkiness and cost, which restrict their widespread use. In recent years, researchers have been focused on developing more compact and affordable optical spectrometers that could be easily deployed on a large scale.
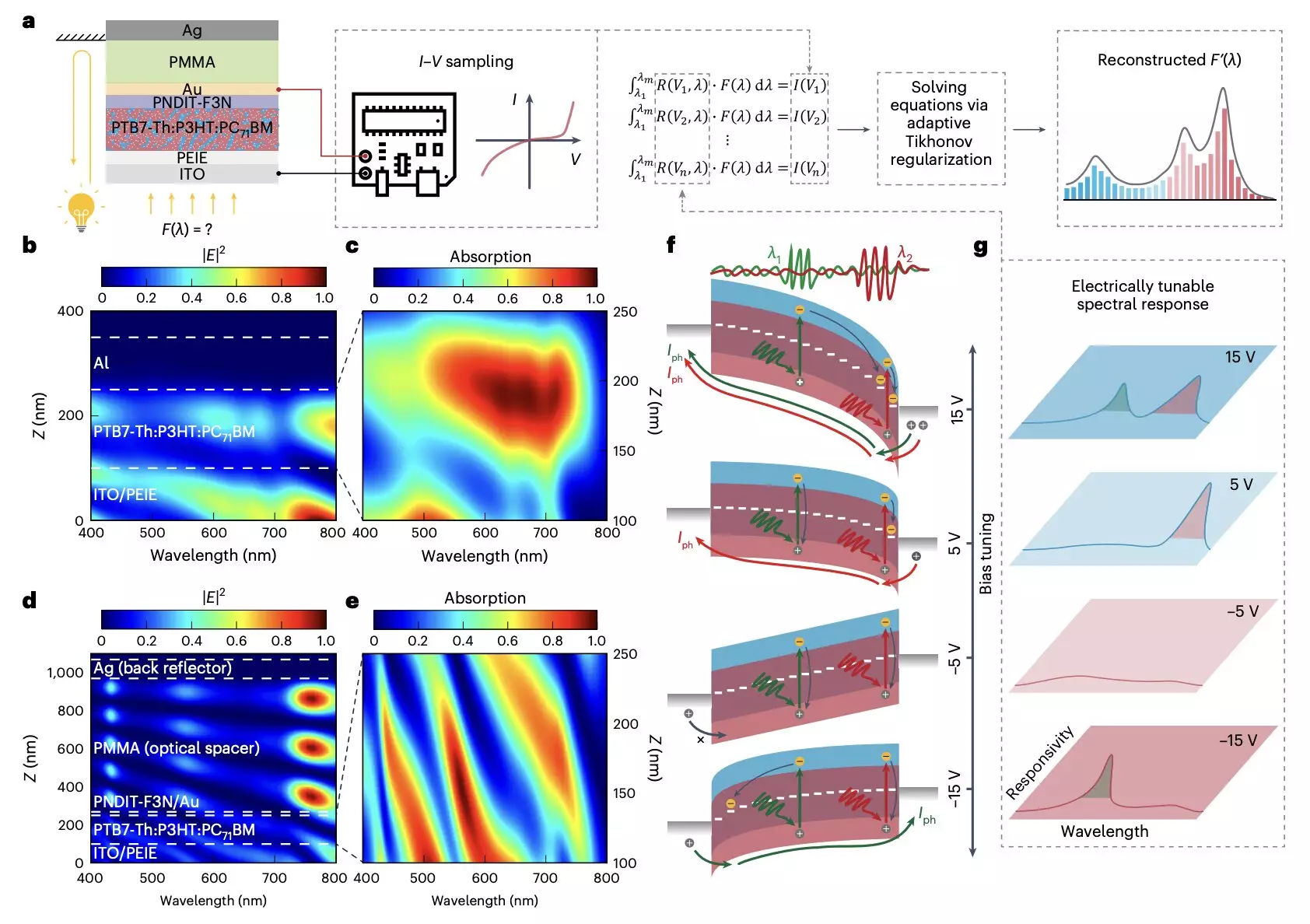
The researchers at the Chinese University of Hong Kong and other institutes in China have recently made significant advancements in this area by introducing a micro-sized, portable, and cost-effective optical spectrometer. This new spectrometer, based on an organic photodetector with a bias-tunable spectral response, offers a promising alternative to conventional designs. The use of arrayed broadband photodetectors, in combination with computational algorithms, has enabled the development of a miniaturized optical spectrometer with a footprint of only 0.0004 cm2.
The key innovation in this new optical spectrometer lies in the manipulation of the wavelength-dependent location of photocarrier generation in photodiodes. By utilizing a trilayer contact consisting of a transparent back contact, an optical spacer, and a back reflector, the researchers were able to create a photomultiplication-type organic photodetector (PM-OPD). This device, combined with a Schottky diode and an organic ternary bulk heterojunction, allows for the computational reconstruction of an incident light spectrum from photocurrents measured under different bias voltages.
The miniaturized optical spectrometer developed by the researchers has been shown to operate across the entire visible spectrum regime with a sub-5-nm resolution. Additionally, it has been utilized to fabricate an 8 x 8 spectroscopic sensor array for hyperspectral imaging, showcasing its potential for detecting unique spectral signatures of specific objects. This innovative approach could pave the way for the development of similar micro-sized and more affordable optical spectrometers, opening up new possibilities for cutting-edge technologies in research and medical practices.
The introduction of miniaturized and cost-effective optical spectrometers holds immense promise for various applications in the future. These devices could revolutionize the field of optical sensing by enabling portable and wearable applications that were previously not feasible with traditional spectrometer designs. Furthermore, the advancements in miniaturization and affordability could inspire the creation of new technologies that enhance research and medical practices, driving innovation in the field of optical spectroscopy.
The development of micro-sized and affordable optical spectrometers represents a significant leap forward in the field of optical sensing. By combining innovative design principles with advanced optical components and computational algorithms, researchers have made it possible to create versatile instruments that offer high performance in a compact form factor. The future of optical spectrometers is indeed bright, with endless possibilities for applications across various industries.

Leave a Reply