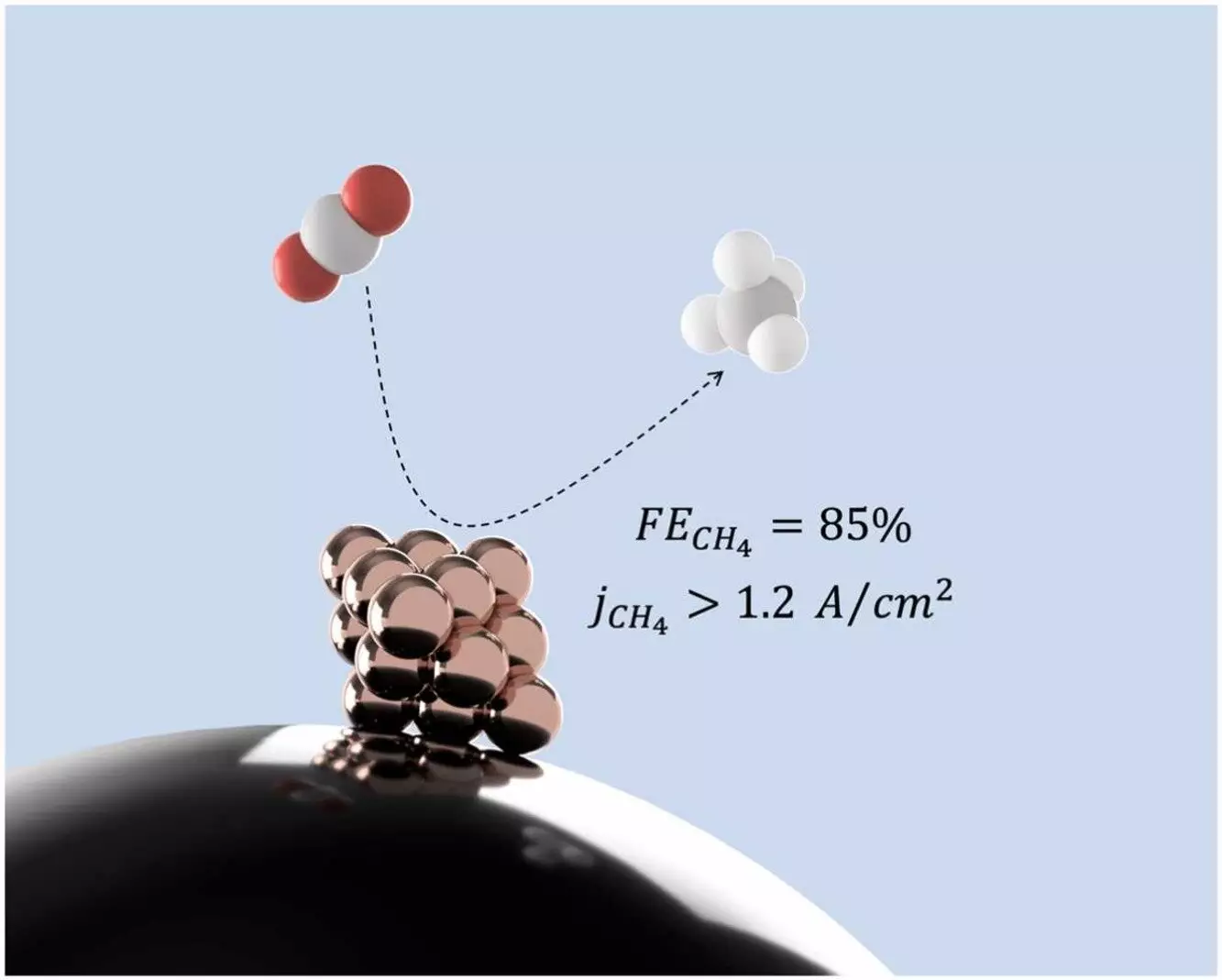
The research conducted by McGill University has paved the way for a groundbreaking discovery in the field of sustainable energy production. By utilizing copper nanoclusters as catalysts, the team has found a way to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into methane, a cleaner source of energy that does not contribute to the carbon emissions in the atmosphere. This innovative process of electrocatalysis offers a promising solution to the pressing issue of climate change caused by carbon in the atmosphere.
One of the most significant advantages of this new method is the creation of a closed “carbon loop.” Unlike traditional methods of producing methane from fossil fuels, which add to the CO2 levels in the atmosphere, the electrocatalysis process allows for the transformation of carbon dioxide into methane. Furthermore, once the methane is utilized, any carbon dioxide released can be captured and recycled back into methane. This cycle effectively eliminates the emission of new carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, making it a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy production method.
According to Salehi, the lead researcher at the Electrocatalysis Lab at McGill University, the key to the success of this process lies in the use of copper nanoclusters. Through their research, the team discovered that extremely small copper nanoclusters are highly effective at producing methane. This finding highlights the importance of the size and structure of the catalyst in determining the outcome of the reaction. By optimizing the design of the copper nanoclusters, the researchers aim to further enhance the efficiency of the catalyst and explore its potential for large-scale industrial applications.
As the research progresses, the team plans to continue refining the catalyst and investigating its practical applications in the energy sector. By leveraging the potential of copper nanoclusters, the researchers hope to open up new pathways for the production of clean and sustainable energy. With their innovative approach to converting carbon into methane, they aspire to contribute to a more environmentally conscious and energy-efficient future.
The development of a methane-producing catalyst using copper nanoclusters represents a significant step forward in the quest for sustainable energy solutions. By harnessing the power of electrocatalysis, researchers are not only addressing the challenges posed by carbon emissions but also creating opportunities for a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy landscape.

Leave a Reply