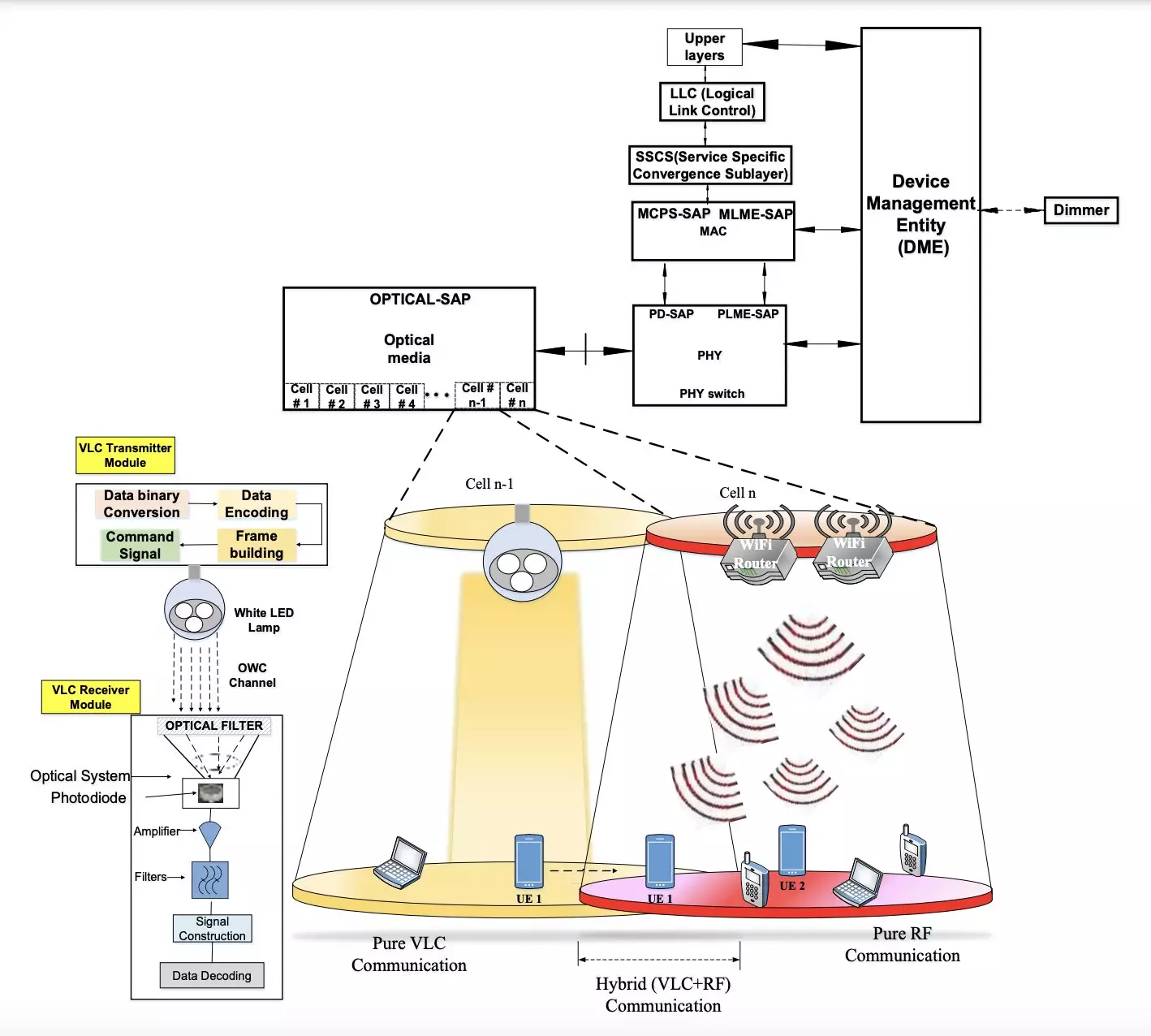
Wireless internet has become an essential part of our daily lives, supporting various activities from professional communications to entertainment. However, the increasing demand for wireless internet access has led to a rise in power consumption and carbon emissions worldwide. In light of this, researchers are exploring energy-efficient techniques to support communication and data transmission. One such solution is visible light communication (VLC), which uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to transmit data. Recently, researchers at Central University (CU) in India introduced a new hybrid approach that combines VLC with Radio Frequency (RF) communication to enable reliable and energy-efficient indoor communication.
The hybrid wireless communication system developed by the researchers consists of two key components: a transmitter and a receiver module. The transmitter is responsible for transmitting binary data through LED-produced light, while the receiver, equipped with a photo-sensitive device, extracts the information from the transmitted light. By utilizing modulation schemes and maintaining a constant power consumption, the system ensures a continuous stream of data transmission.
The proposed hybrid system aims to reduce power consumption and carbon footprint while maintaining the desired Quality of Service (QoS) and Quality of Experience (QoE). Through simulations conducted using various platforms like Python, Scilab, and MathWorks tool, the researchers demonstrated that the hybrid system could enable stable communication in indoor environments with significant energy savings. The system also showed high energy efficiency, low Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), and increased battery lifetime of mobile devices.
The research conducted by the team at Central University (CU) highlights the potential of hybrid wireless communication systems in achieving energy efficiency and reduced electromagnetic radiation. By merging VLC with RF communication, the proposed approach offers a promising solution for indoor communication with lower power consumption. Future studies can further explore and improve upon this hybrid system to enhance wireless communication in various settings.
Overall, while the original article provides valuable insights into the development of a hybrid wireless communication system, there are opportunities for improvement in terms of the structure and presentation of the information. By incorporating clearer subheadings and expanding on the implications of the research findings, the article could engage a wider audience and provide a more thorough analysis of the subject matter.

Leave a Reply