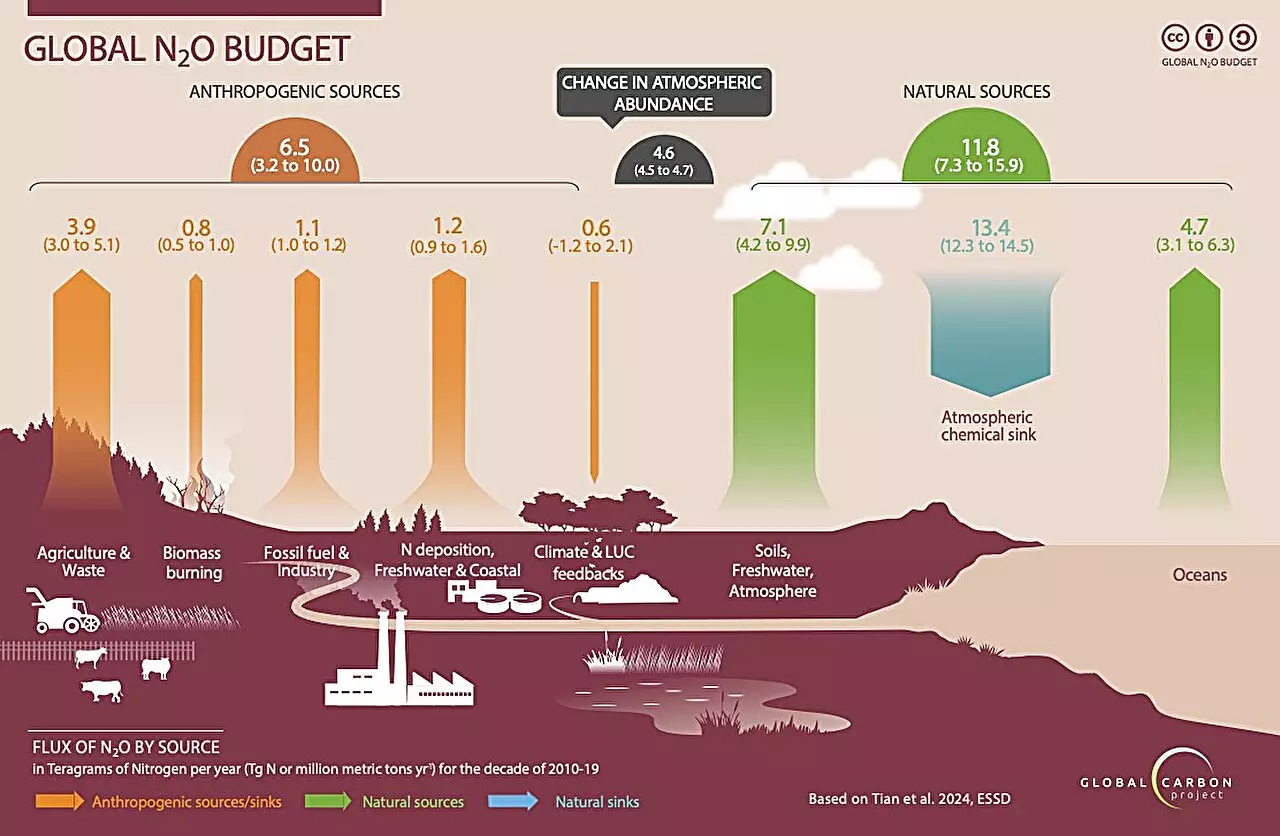
The recent report by the Global Carbon Project sheds light on the concerning trend of nitrous oxide emissions, a powerful greenhouse gas that has continued to increase from 1980 to 2020. With over 10 million metric tons released into the atmosphere in 2020 alone, primarily from farming practices, the impact of these emissions on global warming cannot be ignored. The use of chemical fertilizers and animal waste on croplands has been identified as the main contributor to this issue, highlighting the urgent need for action to curb these emissions.
Agricultural production has been identified as the culprit behind 74% of human-driven nitrous oxide emissions in the 2010s. This revelation underscores the significant impact that farming practices have on the environment and the need for sustainable agricultural methods. The reliance on chemical fertilizers and animal waste has led to a sharp increase in nitrous oxide emissions over the decades, posing a serious threat to the planet’s delicate ecosystem.
Apart from contributing to global warming, excess nitrogen from nitrous oxide emissions also leads to soil, water, and air pollution. In the atmosphere, it depletes the ozone layer and exacerbates climate change, further highlighting the urgent need to address this issue. The concentration of atmospheric nitrous oxide has reached alarming levels, surpassing predictions previously made by climate experts, pointing to the severity of the situation.
Given the dire consequences of unchecked nitrous oxide emissions, it is imperative that immediate action be taken to reduce these harmful gases. The report emphasizes the necessity of limiting global temperature rise to avoid the worst effects of climate change, urging countries to come together to implement effective mitigation strategies. As there are currently no technologies capable of removing nitrous oxide from the atmosphere, reducing emissions is the only viable solution.
The report highlights the top 10 nitrous oxide emission-producing countries, with China, India, and the United States leading the pack. While some countries have made progress in reducing emissions through policy interventions, others continue to face challenges in curbing their nitrous oxide output. Improved agricultural practices, such as limiting the use of nitrogen fertilizers and animal waste, are essential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impact of climate change.
Established in 2001, The Global Carbon Project plays a vital role in analyzing the impact of human activity on greenhouse gas emissions and Earth systems. By producing global budgets for the three dominant greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide – the project provides valuable insights for further research, policy development, and international collaboration. Ongoing assessments and inventories of nitrous oxide sources and sinks are crucial in guiding mitigation efforts and achieving the objectives of the Paris Agreement.
The rise of nitrous oxide emissions poses a significant threat to the planet’s climate and ecosystem. Urgent action is needed to curb these emissions, particularly in the agricultural sector, where significant reductions can be achieved through sustainable practices. By working together and implementing effective mitigation strategies, countries can make a positive impact in reducing nitrous oxide emissions and combating climate change.

Leave a Reply