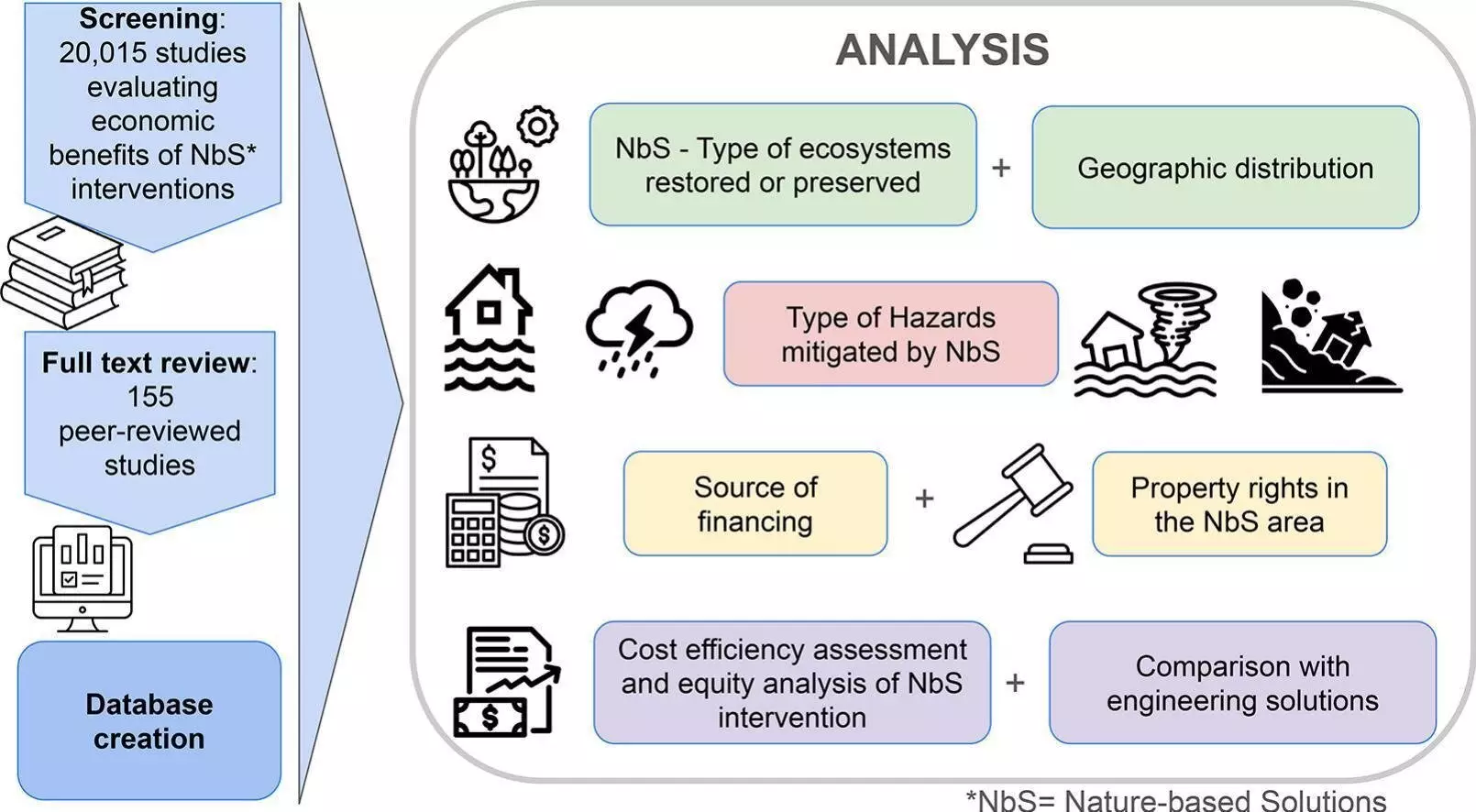
Nature-based solutions (NbS) have been identified as a promising and economically effective method to mitigate risks from various disasters caused by climate change. A recent global assessment led by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst shed light on the potential of NbS in addressing challenges such as floods, hurricanes, heat waves, and landslides, which are predicted to worsen as the planet continues to warm.
The study revealed that NbS, which involve preserving, sustainably managing, or restoring ecosystems to provide benefits to both society and nature, are a cost-effective approach to mitigating hazards. In fact, more than 70% of the reviewed studies found NbS to be consistently cost-effective, with an additional 24% identifying them as such under specific circumstances. This demonstrates the potential of NbS as a viable alternative to engineering-based solutions.
Among the ecosystem-based interventions analyzed in the research, mangroves, forests, and coastal ecosystems were highlighted as the most effective in mitigating hazards. Studies comparing NbS with engineering solutions also indicated that NbS were either equally or more effective in addressing natural disasters. This suggests that investing in the preservation and restoration of natural habitats can yield significant benefits in terms of hazard mitigation.
While the hazard-mitigation benefits of NbS have been well-documented, the study pointed out that the additional environmental and socioeconomic advantages are often underestimated. Factors such as biodiversity conservation, climate mitigation, and support for marginalized communities are challenging to quantify and thus tend to be overlooked in assessments of NbS. This underscores the need for a more comprehensive evaluation of the broader benefits that NbS offer.
One of the key challenges identified in the research is the financing of NbS, which has predominantly relied on public funding. Despite the involvement of private property in some interventions, the public sector has shouldered most of the financial burden. To scale up NbS globally and maximize their impact, it is crucial to attract additional funding, particularly from the private sector. A more balanced approach to financing NbS is essential for their widespread adoption.
The assessment of scientific literature on NbS highlights the immense potential of nature-based solutions in mitigating the impact of natural disasters. By recognizing the economic effectiveness and multifaceted benefits of NbS, policymakers, and stakeholders can make more informed decisions about sustainable disaster risk reduction strategies. Moving forward, there is a need for increased investment in NbS and a shift towards a more holistic approach that considers the environmental, social, and economic aspects of these solutions. Embracing nature-based solutions can pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable future in the face of climate change-induced challenges.

Leave a Reply