In the expansive realm of wave physics, the ability to meticulously control wave transport and localization remains a top-tier ambition among researchers. This discipline encompasses a number of subfields, including solid-state physics, matter-wave phenomena, and photonics. A particularly captivating phenomenon within this domain is the Bloch oscillation (BO). This occurrence describes the rhythmic motion of electrons in solids when subjected to a consistent direct current (DC) under an electric field. However, the exploration doesn’t end there; an even more complex image emerges with Super-Bloch oscillations (SBOs), a vibrant rendition that has largely flown under the radar due to the intricacies involved in its experimental deployment.
The Intricacies of Super-Bloch Oscillations
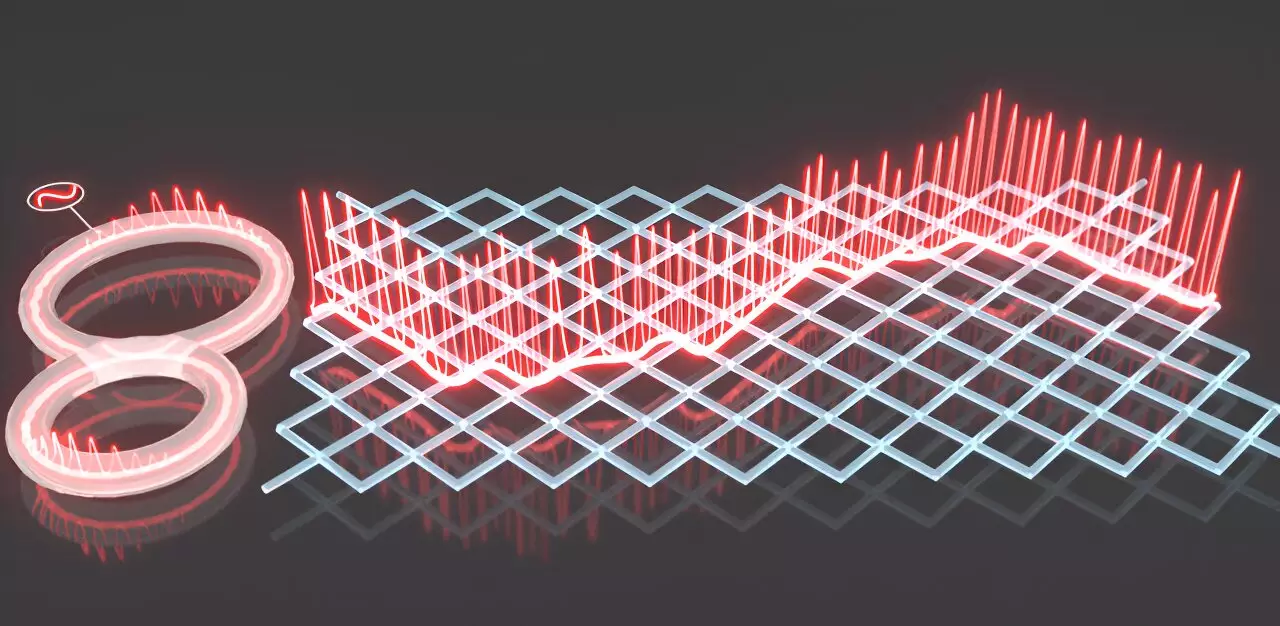
Super-Bloch oscillations stand as an exaggerated manifestation of traditional Bloch oscillations. They arise when a system is influenced by both a direct current field and a nearly detuned alternating current (AC) field. Despite their potential, SBOs lack the recognition they deserve largely because collecting empirical data about them poses significant challenges. These challenges stem from the need for a notably extended coherence time for the particles involved. A remarkable aspect of SBOs is the phenomenon of coherent oscillation inhibition, which allows for the localization of oscillation patterns, leading to an intriguing scenario where oscillation amplitude can experience a complete diminishment, a condition famously referred to as the “collapse” of SBOs.
In a landscape where traditional methods falling short, researchers have been pushing boundaries to uncover this elusive SBO collapse phenomenon. Their previous efforts yielded data primarily from standard sinusoidal AC driving scenarios. Unfortunately, this limited scope left a myriad of potential for varied AC formats unexplored and the possibilities of utilizing SBOs for versatile wave manipulation largely untapped.
Groundbreaking Research from Leading Institutions
Recently, a promising study has emerged from a collaboration involving the Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, the School of Physics at Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and the Polytechnic University of Milan. Documented in the journal Advanced Photonics, this research endeavors to surmount hurdles that have historically hindered SBO examinations. By ingeniously integrating a DC driving field with a nearly detuned AC driving field within a synthetic temporal lattice, the researchers transcended existing limitations. For the first time, they recorded the collapse effect of SBOs and successfully broadened their research to encompass arbitrary wave driving conditions.
The results uncovered in this study present profound implications for wave physics. By exercising control over the synthetic electric fields, the team observed distinct characteristics indicative of SBO collapse, including decreasing oscillation amplitudes and reversals in the oscillation direction at predetermined driving levels. Notably, a specific amplitude-to-frequency ratio of AC driving field that aligns with the first-order Bessel function was critical in prompting SBO collapse. This pivotal finding marks a significant step forward, showcasing how using mathematical constructs from wave theory can directly impact tangible phenomena observed in experiments.
Theoretical Framework vs. Experimental Realities
While this study served to underscore the remarkable nature of SBOs, it also shone a light on the gap between theoretical explorations and experimental realities in wave physics. Much of the existing theoretical framework centered around sinusoidal AC driving has overlooked the vast landscape of other possible driving formats. However, this recent research illuminates a path forward, revealing generalized SBOs with customizable collapse conditions. This flexibility could unlock numerous applications spanning communications, quantum computing, and material sciences, offering exciting horizons for future investigations.
Moreover, the assessment of oscillation patterns through a Fourier spectrum analysis confirms the complexities interwoven within these phenomena. By dissecting the intricacies of the oscillation results, researchers glean a greater understanding of the underlying mechanics at play. The rapidly oscillating characteristics in SBOs and their extraordinary capacity to produce a collapse offer an exhilarating glimpse into how meticulous adjustments to external conditions can unlock profound changes in wave behavior.
Overall, the advances in understanding Super-Bloch oscillations open the door not only to innovative applications and research endeavors but also to the engaging mystery of coherent transport phenomena. The journey is far from over, yet each discovery pushes the boundaries of what once was seemingly unimaginable within the field of wave physics.

Leave a Reply